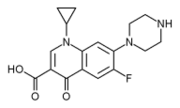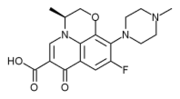
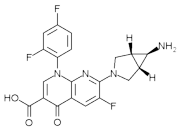
The quinolones are a family of broad-spectrum antibiotics. The parent of the group is nalidixic acid. The majority of quinolones in clinical use belong to the subset of fluoroquinolones, which have a fluoro group attached the central ring system.
Contents |
Mechanism
Quinolones and fluoroquinolones are bactericidal drugs, actively killing bacteria. Quinolones inhibit the bacterial DNA gyrase or the topoisomerase IV enzyme, thereby inhibiting DNA replication and transcription. Quinolones can enter cells easily and therefore are often used to treat intracellular pathogens such as Legionella pneumophila and Bacillus anthracis.
Adverse effects
Quinolone antibiotics were once considered relatively safe, but several side effects have become evident with experience. For example, numerous case reports have implicated their use since 1965 in spontaneous tendon ruptures or damage, especially with the concurrent use of a systemic corticosteroid. In the fall of 2004, the Food and Drug Administration upgraded the warnings found within the package inserts for all drugs within this class regarding such serious adverse reactions.
- Peripheral neuropathy (irreversible nerve damage): "Rare cases of sensory or sensor motor axonal polyneuropathy affecting small and or large axons resulting in paresthesias, hypoaesthesias, dysesthesias, and weakness have been reported in patients taking quinolones. Therapy should be discontinued if the patient experiences symptoms of neuropathy including pain, burning, tingling, numbness and or weakness or is found to have deficits in light touch, pain, temperature, position sense, vibratory sensation, and or motor strength in order to prevent the development of an irreversible condition."
- Tendon damage: "Ruptures of the shoulder, hand, Achilles tendon or other tendons that require surgical repair or resulted in prolonged disability have been reported in patients receiving quinolones. Post-marketing surveillance reports indicate that this risk may be increased in patients receiving concomitant corticosteroids, especially the elderly. Fluoroquinolone therapy should be discontinued if the patient experiences pain, inflammation, or rupture of a tendon. Patients should rest and refrain from exercise until diagnosis of tendonitis or tendon rupture had been excluded. Tendon rupture can occur during or after therapy with quinolones."
Other problems include:
- Heart problems (prolonged QT Interval / Torsades de
pointes)
Pseudomembranous colitis
Rhabdomyolysis (muscle wasting)
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Lowered seizure threshold
Resistance
Resistance to quinolones can develop rapidly, even during a course of treatment. Numerous pathogens, including Staphylococcus aureus, enterococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Streptococcus pyogenes now exhibit resistance worldwide.[1] Widespread veterinary usage of quinolones, particularly in Europe, has been implicated.
Generations
The quinolones are divided into generations based on their antibacterial spectrum. The earlier generation agents are generally more narrow spectrum than the later ones.
1st generation
- cinoxacin (Cinoxacin®)
flumequine (Flubactin®) (*Veterinary use*)
nalidixic acid (NegGam®, Wintomylon®)
oxolinic acid
piromidic acid
pipemidic acid
2nd generation
- ciprofloxacin (Cipro®, Ciproxin®)
- enoxacin (Enroxil®, Penetrex®)
fleroxacin (Megalone®)
levofloxacin (Cravit®, Levaquin®, Quixin®)
lomefloxacin (Maxaquin®)
nadifloxacin
norfloxacin (Noroxin®, Quinabic®, Janacin®)
ofloxacin (Floxin®, Oxaldin®, Tarivid®)
pefloxacin
rufloxacin
3rd generation
- balofloxacin
gatifloxacin (Tequin®)
grepafloxacin (Raxar®)
pazufloxacin Mesilate
sparfloxacin (Zagam®)
temafloxacin
tosufloxacin
4th generation
- clinafloxacin
gemifloxacin (Factive®)
moxifloxacin (Avelox®)
Gatifloxacin (Zymar®)
sitafloxacin
trovafloxacin (Trovan®)
In development
- ecinofloxacin
prulifloxacin
Veterinary use
The quinolones have been widely used in agriculture and several agents exist which have veterinary but not human use.
- danofloxacin (Advocin®, Advocid®) (*Veterinary use*)
difloxacin (Dicural®, Vetequinon®)
enrofloxacin (Baytril®)
marbofloxacin (Marbocyl®, Zenequin®) (*Veterinary use*)
orbifloxacin (Orbax®, Victas®) (*Veterinary use*)
sarafloxacin (Floxasol®, Saraflox®, Sarafin®) (*Veterinary use*)
External links
- Fact Sheet: Quinolones
- Fluoroquinolone-Induced Tendinopathy: What do we know? Richard M. Harrell, MD.
- Fluoroquinolones "Family Practice Notebook" entry page for Fluoroquinolones
- Structure Activity Relationships "Antibacterial Agents; Structure Activity Relationships," André Bryskier MD
- [1] "The Adverse Drug Reactions of the Fluoroquinolones" entry page for Fluoroquinolone Toxicity Research Foundation webpages




 216.73.216.133
216.73.216.133 User Stats:
User Stats:
 Today: 0
Today: 0 Yesterday: 0
Yesterday: 0 This Month: 0
This Month: 0 This Year: 0
This Year: 0 Total Users: 117
Total Users: 117 New Members:
New Members:
 216.73.xxx.xxx
216.73.xxx.xxx
 Server Time:
Server Time: