| Silver nitrate | ||
|---|---|---|
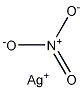 |
||
| General | ||
| Molecular formula | AgNO3 | |
| Molar mass | 169.8731 g/mol | |
| Appearance | white solid | |
| CAS number | [7761-88-8] | |
| Properties | ||
| Density and phase | 4.35 g/cm3, solid | |
| Solubility in water | 219 g/100 ml (20 °C °C) | |
| Melting point | 212 °C | |
| Boiling point | 444 °C decomp. | |
| Structure | ||
|
Coordination geometry |
Trigonal Pyramidal | |
| Crystal structure | rhombohedral | |
| Hazards | ||
| MSDS | External MSDS | |
| EU classification | Corrosive (C) Dangerous for the environment (N) |
|
| NFPA 704 |
|
|
| R-phrases | R34, R50/53 | |
| S-phrases |
S1/2,
S26,
S45, S60, S61 |
|
| Flash point | non-flammable | |
| Related compounds | ||
| Other cations | Copper(II) nitrate | |
|
Except where noted otherwise, data are given
for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) |
||
Silver nitrate is a chemical compound with chemical formula AgNO3. This nitrate of silver is a light-sensitive ingredient in photographic film and is a poisonous, corrosive compound. Silver nitrate crystals can be produced by dissolving silver in nitric acid and evaporating the solution. The compound notably stains skin a greyish or black color that is made visible after exposure to sunlight.

When making photographic film, silver nitrate is reacted with halide salts of sodium or potassium to form insoluble silver halide in situ in photographic gelatin, which is then applied to strips of tri-acetate or polyester. Photons from sunlight, X-rays or other sources, initiate a chemical chain reaction: when photons strike silver nitrate molecules, they free electrons from the halide ions. These free electrons roam through the crystal and settle in structural imperfections called sensitivity specks. These specks attract positive silver ions, which are then neutralized to form groups of stable silver atoms, creating a latent image that is chemically developed to reveal a photographic image.
Silver nitrate has antiseptic properties. It is sometimes dropped into newborn babies' eyes at birth to prevent contraction of gonorrhoea or chlamydia from the mother. Disposal of even small quantities of silver nitrate in toilets connected to a septic tank is guaranteed to destroy the septic bacteria and necessitate pumping out and flushing and seeding with fresh bacteria.
Fused silver nitrate, shaped into sticks, was traditionally called lunar caustic. It is used as a cauterizing agent.
In histology, silver nitrate is used for silver staining, for demonstrating proteins and nucleic acids. For this reason it is also used to demonstrate proteins in PAGE gels. It is also used as a stain in scanning electron microscopy.
Silver nitrate is used to prepare some silver-based explosives, such as the fulminate, azide, or acetylide, through a precipitation reaction.
Silver nitrate may be used to electroplate metals if dissolved in water.




 216.73.216.103
216.73.216.103 User Stats:
User Stats:
 Today: 0
Today: 0 Yesterday: 0
Yesterday: 0 This Month: 0
This Month: 0 This Year: 0
This Year: 0 Total Users: 117
Total Users: 117 New Members:
New Members:
 216.73.xxx.xxx
216.73.xxx.xxx
 Server Time:
Server Time:
