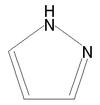
| Pyrazole | |
|---|---|
| Chemical name | Pyrazole |
| Chemical formula | C3H4N2 |
| Synonyms | 1,2 diazole, Pyrazol |
| Molecular mass | 68.07 g/mol |
| Melting point | 66-70 °C |
| Boiling point | 186-188 °C |
| Density | x.xxx g/cm3 |
| CAS number | 288-13-1 |
| SMILES | C1=CC=NN1 |
 |
|
| Disclaimer and references | |
Pyrazole refers both to the class of simple aromatic ring organic compounds of the heterocyclic series characterized by a 5-membered ring structure composed of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms in adjacent positions and to the unsubstituted parent compound. Being so composed and having pharmacological effects on humans, they are classified as alkaloids although they are not known to occur in nature.
Pyrazoles are produced synthetically through the reaction of α,β-unsaturated aldehydes with hydrazine and subsequent dehydrogenation.
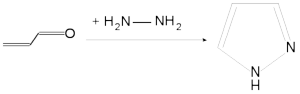
Pyrazoles are used for their analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antiarrhythmic, tranquilizing, muscle relaxing, psychoanaleptic, anticonvulsant, monoamineoxidase inhibiting, antidiabetic and antibacterial activities.
Structurally related compounds are pyrazoline and pyrazolidine.





 216.73.216.103
216.73.216.103 User Stats:
User Stats:
 Today: 0
Today: 0 Yesterday: 0
Yesterday: 0 This Month: 0
This Month: 0 This Year: 0
This Year: 0 Total Users: 117
Total Users: 117 New Members:
New Members:
 216.73.xxx.xxx
216.73.xxx.xxx
 Server Time:
Server Time: