 |
|
|
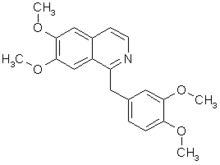
Papaverine
|
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| 1-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-6,7-dimethoxy-isoquinoline | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 61-25-6 |
| ATC code | A03AD01 G04BE02 |
| PubChem | 4680 |
| DrugBank | APRD00628 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C20H21NO4[1] |
| Mol. weight | 339.385 g/mol[1] |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 80%[3] |
| Protein binding | ~90% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic[3] |
| Half life | 1.5-2 hours[3] |
| Excretion | Renal[3] |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. | USA: C[4] |
| Routes | Oral, intravenous, intramuscular, rectal,[5] intracavernosal |
Papaverine is an opium alkaloid used primarily in the treatment of visceral spasm, vasospasm (especially those involving the heart and the brain), and occasionally in the treatment of erectile dysfunction[3]. While it is found in the opium poppy, papaverine differs in both structure and pharmacological action from the other opium alkaloids.
Contents |
Uses
Papaverine is approved to treat spasms of the gastointestinal tract, bile ducts and ureter and for use as a cerebral and coronary vasodilator[3] in subarachnoid hemorrhage (combined with balloon angioplasty)[6] and coronary artery bypass surgery[7]. Papaverine may also be used as a smooth muscle relaxant in microsurgery where it is applied directly to blood vessels.
The in vivo mechanism of action is not entirely clear, but an inhibition of the enzyme phosphodiesterase causing elevation of cyclic AMP levels is significant. It may also alter mitochondrial respiration.
Side effects
Frequent side effects of papaverine treatment include polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, constipation, interference with sulphobromophthalein[8] retention test (used to determine hepatic function), increased transaminase levels, increased alkaline phosphatase levels, hyperbilirubinemia, somnolence, and vertigo[3].
Rare side effects include flushing of the face, hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating), cutaneous eruption, arterial hypotension, tachycardia, lack of appetite, jaundice, eosinophilia, thrombopenia, mixed hepatitis, headache, allergic reaction, chronic active hepatitis,[3] and paradoxical aggravation of cerebral vasospasm[9].
Formulations and Tradenames
Papaverine is available as a conjugate of hydrochloride, codecarboxylate, adenylate, and teprosylate[10]. It was also once available as a salt of hydrobromide, camsylate, cromesilate, nicotinate, and phenylglycolate. The hydrochloride salt is available for intramuscular, intravenous, rectal and oral administration.[5] The teprosylate is available in intravenous, intramuscular, and orally administered formulations[11]. The codecarboxylate is available in oral form, only,[12] as is the adenylate[13].
The codecarboxylate is sold under the name Albatran®,[14] the adenylate as Dicertan®,[15] and the hydrochloride salt is sold variously as Artegodan® (Germany), Cardioverina® (countries outside Europe and the United States), Dispamil® (countries outside Europe and the United States), Opdensit® (Germany), Panergon® (Germany), Paverina Houde® (Italy, Belgium), Pavacap (United States), Pavadyl® (United States), Papaverin-Hamelin® (Germany), Paveron® (Germany), Spasmo-Nit® (Germany),[5] Cardiospan®, Papaversan®, Cepaverin®, Cerespan®, Drapavel®, Forpaven®, Papalease®, Pavatest®, Paverolan®, Therapav® (France[16]), Vasospan®, Cerebid®, Delapav®, Dilaves®, Durapav®, Dynovas®, Optenyl®, Pameion®, Papacon®, Pavabid®, Pavacen®, Pavakey®, Pavased®, Pavnell®, Alapav®, Myobid®, Vasal®, Pamelon®, Pavadel®, Pavagen®, Ro-Papav®, Vaso-Pav®, Papanerin-hcl®, Qua bid®, Papital T.R.®, Paptial T.R.®, Pap-Kaps-150®.[17]
References
- a b c SID 544606 -- PubChem Substance Summary. Retrieved on 25 September 2005. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- a Papaverine Material Safety Data Sheet. Retrieved on 25 September 2005.
- a b c d e f g h Unknown (2000). PAPAVERINE. Molécule(s) de base : PAPAVERINE. Biam. Retrieved on 25 September 2005. (French)
- a Unknown (2004). Who should not take papaverine?. papaverine Consumer Drug Information. Cerner Multum, Inc. Retrieved on 26 September 2005.
- a b c Unknown (1999). PAPAVERINE CHLORHYDRATE. Molécule(s) de base : PAPAVERINE. Biam. Retrieved on 25 September 2005. (French)
- a Liu, James K.; Couldwell, William T (2005). "Intra-arterial papaverine infusions for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm induced by aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage". Neurocritical Care 2 (2): 124-32. PMID 16159054. Fulltext options List of Library Holdings
- a Takeuchi K, Sakamoto S, Nagayoshi Y, Nishizawa H, Matsubara J (2004). "Reactivity of the human internal thoracic artery to vasodilators in coronary artery bypass grafting". European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 26 (5): 956-9. PMID 15519189. Fulltext options List of Library Holdings
- a SID 149219 -- PubChem Substance Summary. Retrieved on 26 September 2005. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- a Clyde BL, Firlik AD, Kaufmann AM, Spearman MP, Yonas H (1996). "Paradoxical aggravation of vasospasm with papaverine infusion following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Case report". Journal of Neurosurgery 84 (4): 690-5. PubMed
- a Molécule de base : PAPAVERINE. Retrieved on 26 September 2005. Biam.
- a Unknown (1999). PAPAVERINE TEPROSILATE. Molécule(s) de base : PAPAVERINE. Biam. Retrieved on 26 September 2005. (French)
- a Unknown (1998). PAPAVERINE CODECARBOXYLATE. Molécule(s) de base : PAPAVERINE. Biam. Retrieved on 26 September 2005. (French)
- a Unknown (1998). PAPAVERINE ADENYLATE. Molécule(s) de base : PAPAVERINE. Biam. Retrieved on 26 September 2005. (French)
- a SID 660773 PubChem Substance Summary. Retrieved on 25 September 2005. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- a SID 660767 -- PubChem Substance Summary. Retrieved on 25 September 2005. National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- a THERAPAV (PRODUIT PUR) - Détail. Retrieved on 26 September 2005. CSST - Service du répertoire toxicologique. (French)
- a SID 660767 -- PubChem Substance Summary - Depositor-Supplied Synonyms: All. Retrieved on 26 September 2005. National Center for Biotechnology Information.




 216.73.216.133
216.73.216.133 User Stats:
User Stats:
 Today: 0
Today: 0 Yesterday: 0
Yesterday: 0 This Month: 0
This Month: 0 This Year: 0
This Year: 0 Total Users: 117
Total Users: 117 New Members:
New Members:
 14.171.xx.xxx
14.171.xx.xxx
 Server Time:
Server Time: