| Niacin | |
|---|---|
 |
|
| Systematic name | 3-Pyridinecarboxylic acid |
| Chemical formula | C6H5NO2 |
| Molecular mass | 123.11 g/mol |
| Melting point | 236.6 °C |
| CAS number | [59-67-6] |
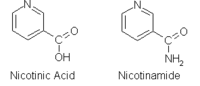
Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid or vitamin B3, is a water-soluble vitamin whose derivatives such as NADH, NAD, NAD+, and NADP play essential roles in energy metabolism in the living cell and DNA repair.[1] The designation vitamin B3 also includes the amide form, nicotinamide or niacinamide, whose chemical formula is C6H6N2O. Severe lack of niacin causes the deficiency disease pellagra, wherein a mild deficiency slows down the metabolism decreasing cold tolerance. The recommended daily allowance of niacin is 2-12 mg a day for children, 14 mg a day for women, 16 mg a day for men, and 18 mg a day for pregnant or breast-feeding women.[2]
Contents |
Discovery
Nicotinic acid was first discovered from the oxidation of nicotine. When the properties of nicotinic acid were discovered, it was thought prudent to choose a name to dissociate it from nicotine and to avoid the idea that either smoking provided vitamins or that wholesome food contained a poison. The resulting name 'niacin' was derived from nicotinic acid + vitamin. Vitamin B3 is also referred to as "vitamin PP", a name derived from the obsolete term "pellagra-preventing factor."
Bioavailability
The liver can synthesize niacin from the essential amino acid tryptophan (see below), but the synthesis is extremely slow; 60 mg of tryptophan are required to make one milligram of niacin. Dietary niacin deficiency tends to occur only in areas where people eat corn, the only grain low in niacin, as a staple food, and that don't use lime during maize (corn) meal/flour production. Alkali lime releases the tryptophan from the corn so that it can be absorbed in the gut, and converted to niacin.[3]
Biosynthesis
The 5-membered aromatic heterocycle of the essential amino acid, tryptophan, is cleaved and rearranged with the alpha amino group of tryptophan into the 6-membered aromatic heterocycle of niacin. By the following reaction:
Tryptophan --> Kynurenine --> 3-hydroxy kynurenine* --(B6 enzyme needed)--> Niacin
(*) from this intermediary xanthurenic acid is formed
Food Sources
| Animal products: | Fruits and vegetables: | Seeds: | Fungi: |
|---|---|---|---|
|
liver, heart and kidney chicken fish: tuna, salmon milk eggs |
leaf vegetables broccoli tomatoes carrots dates sweet potatoes asparagus avocados |
nuts whole grain products legumes saltbush seeds |
mushrooms brewer's yeast |
Other uses
Niacin plays an important role in the production of several sex and stress-related hormones, particularly those made by the adrenal gland. It is also plays a role in removing toxic and harmful chemicals from the body.[3] There is evidence that doses of 500-1000mg can terminate a bad trip on LSD, a synthetic indole, or enhance the MDMA experience.
Niacin, when taken in large doses, increases the level of High density lipoprotein (HDL)or "good" cholesterol in blood, and is sometimes prescribed for patients with low HDL, and at high risk of heart attack.[4] Niacin (but not niacinamide) is also used in the treatment of hyperlipidemia because it reduces Very low density lipoprotein (VLDL) secretion, a precursor of Low density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad" cholesterol, from the liver and inhibits cholesterol synthesis.[5] However, niacin is toxic to the skin and liver in overdose, and high doses of niacin should only be taken when prescribed by a knowledgeable health care provider. Studies in laboratory animals have demonstrated behavioral changes when large doses of niacin are given.[6]
Industrial use
Nicotinic acid reacts with hemoglobin and myoglobin in meat to form a brightly coloured complex, and thus has been used as a food additive, typically to improve the colour of minced (ground) meat. Niacin is licensed as a food colouring agent in some countries. i
References
- ^ Northwestern University Nutrition
- ^ Jane Higdon, "Niacin", Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute
- ^ a b Vitamin B3 University of Maryland Medical Center.
- ^ Postgraduate Medicine
- ^ Katzung and Trevors Pharmacology Examination and Board Review 7th edition, Authors: Trevor, Anthony J. Katzung, Bertram G. and Masters, Susan B., Lange Medical Books/ McGraw-Hill 2005
- ^ Sullivan, WT (June 10, 1958). "Behavioral changes in rats and guinea pigs induced by the administration of indole 3-acetic acid and 6-aminonicotinamide". The Journal of Nutrition: 199-209. Retrieved on September 4, 2006.




 216.73.216.133
216.73.216.133 User Stats:
User Stats:
 Today: 0
Today: 0 Yesterday: 0
Yesterday: 0 This Month: 0
This Month: 0 This Year: 0
This Year: 0 Total Users: 117
Total Users: 117 New Members:
New Members:
 216.73.xxx.xxx
216.73.xxx.xxx
 Server Time:
Server Time: