 |
|
|
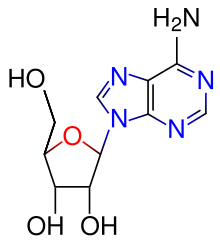
Adenosine
|
|
| Systematic (IUPAC) name | |
| (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)- 5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 58-61-7 |
| ATC code | C01EB10 |
| PubChem | 60961 |
| DrugBank | APRD00132 |
| Chemical data | |
| Formula | C10H13N5O4 |
| Mol. weight | 267.242 g/mol |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ? |
| Metabolism | ? |
| Half life | ? |
| Excretion | ? |
| Therapeutic considerations | |
| Pregnancy cat. | ? |
| Legal status | |
| Routes | ? |
Adenosine is a nucleoside comprised of adenine attached to a ribose (ribofuranose) moiety via a β-N9-glycosidic bond.
Adenosine plays an important role in biochemical processes, such as energy transfer - as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) - as well as in signal transduction as cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cAMP.
Contents |
Pharmacological effects
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Adenosine is a potent anti-inflammatory agent, acting at its four G-protein coupled receptors. Topical treatment of adenosine to foot wounds in diabetes mellitus has been shown in lab animals to drastically increase tissue repair and reconstruction. Topical administration of adenosine for use in wound healing deficiencies and diabetes mellitus in humans is currently under clinical investigation.
Action on the heart
When administered intravenously, adenosine causes transient heart block in the AV node. It also causes endothelial dependent relaxation of smooth muscle as is found inside the artery walls. This causes dilatation of the "normal" segments of arteries where the endothelium is not separated from the tunica media by atherosclerotic plaque. This feature allows physicians to use adenosine to test for blockages in the coronary arteries, by exaggerating the difference between the normal and abnormal segments.
In individuals suspected of suffering from a supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify the rhythm. Certain SVTs can be successfully terminated with adenosine. This includes any re-entrant arrhythmias that require the AV node for the re-entry (e.g., AV reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT). In addition, atrial tachycardia can sometimes be terminated with adenosine.
Adenosine has a direct effect on atrial tissue causing a shortening of the refractory period. When administered via a central lumen catheter, adenosine has been shown to initiate atrial fibrillation because of its affect on atrial tissue. In individuals with accessory pathways, the onset of atrial fibrillation can lead to a life threatening ventricular fibrillation.
Fast rhythms of the heart that are confined to the atria (e.g., atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter) or ventricles (e.g., monomorphic ventricular tachycardia) and do not involve the AV node as part of the re-entrant circuit are not typically affected by adenosine.
Because of the effects of adenosine on AV node-dependent SVTs, adenosine is considered a class V antiarrhythmic agent.
The pharmacological effects of adenosine are blunted in individuals who are taking methylxanthines (e.g., caffeine (found in coffee) and theophylline (found predominantly in tea)).
Dosage
When given for the evaluation or treatment of an SVT, the initial dose is 6 mg, given as a fast IV push. Due to adenosine's extremely short half-life, start the IV line as proximal to the heart as possible, such as the antecubital fossa. If this has no effect (e.g., no evidence of transient AV block), a 12mg dose can be given 1-2 minutes after the first dose. If the 12mg dose has no effect, a second 12mg dose can be administered 1-2 minutes after the previous dose. Some clinicians may prefer to administer a higher dose (typically 18 mg), rather than repeat a dose that apparently had no effect. When given to dilate the arteries, such as in a "stress test", the dosage is typically 0.14 mg/kg/min, administered for 4 or 6 minutes, depending on the protocol.
Consider increasing the recommended dose in patients on theophylline since methylxanthines prevent binding of adenosine at receptor sites. Consider decreasing the dose in patients on dipyridamole (Persantine) and diazepam (Valium) because adenosine potentiates the effects of these drugs.
Consider decreasing the recommended dose in half in patients who are presenting Congestive Heart Failure, Myocardial Infarction, shock, hypoxia, and/or hepatic or renal insufficiency.
Consider decreasing the recommended dose in half for elderly patients.
Drug Interactions
beta blockers and dopamine may precipitate toxicity in the patient.
Contraindications
Poison/Drug induced tachycardia, Asthma (relative contraindication), 2nd or 3rd degree heart block, Atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, Ventricular tachycardia, Sick sinus syndrome, Stokes-Adams Attack, Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome, bradycardia with Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs).
Side effects
Many individuals experience facial flushing, lightheadedness, diaphoresis, or nausea after administration of adenosine. These symptoms are transitory, usually lasting less than one minute.
Metabolism
When adenosine enters the circulation, it is broken down by adenosine deaminase, which is present in red cells and the vessel wall.
Dipyridamole, an inhibitor of adenosine deaminase, allows adenosine to accumulate in the blood stream. This causes an increase in coronary vasodilatation.
External links
- Computational Chemistry Wiki
- Link page to external chemical sources.




 216.73.216.133
216.73.216.133 User Stats:
User Stats:
 Today: 0
Today: 0 Yesterday: 0
Yesterday: 0 This Month: 0
This Month: 0 This Year: 0
This Year: 0 Total Users: 117
Total Users: 117 New Members:
New Members:
 216.73.xxx.xxx
216.73.xxx.xxx
 Server Time:
Server Time: